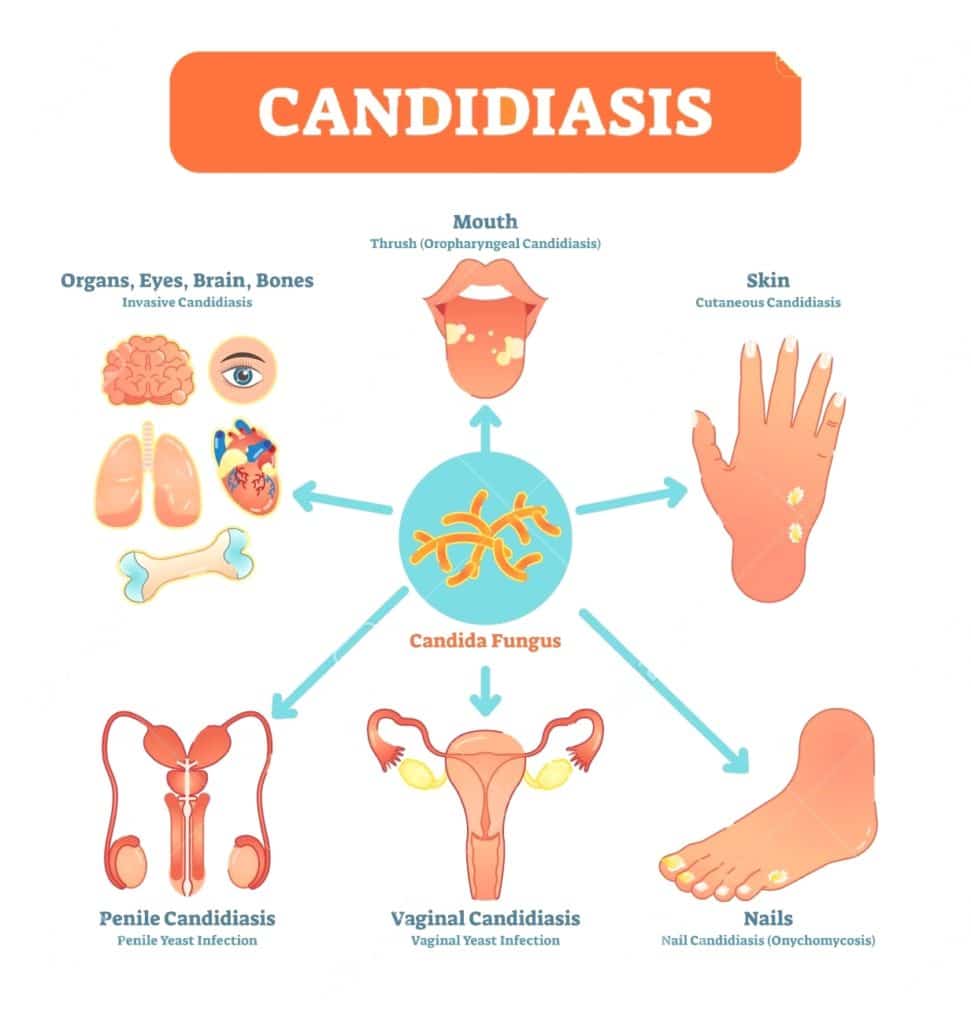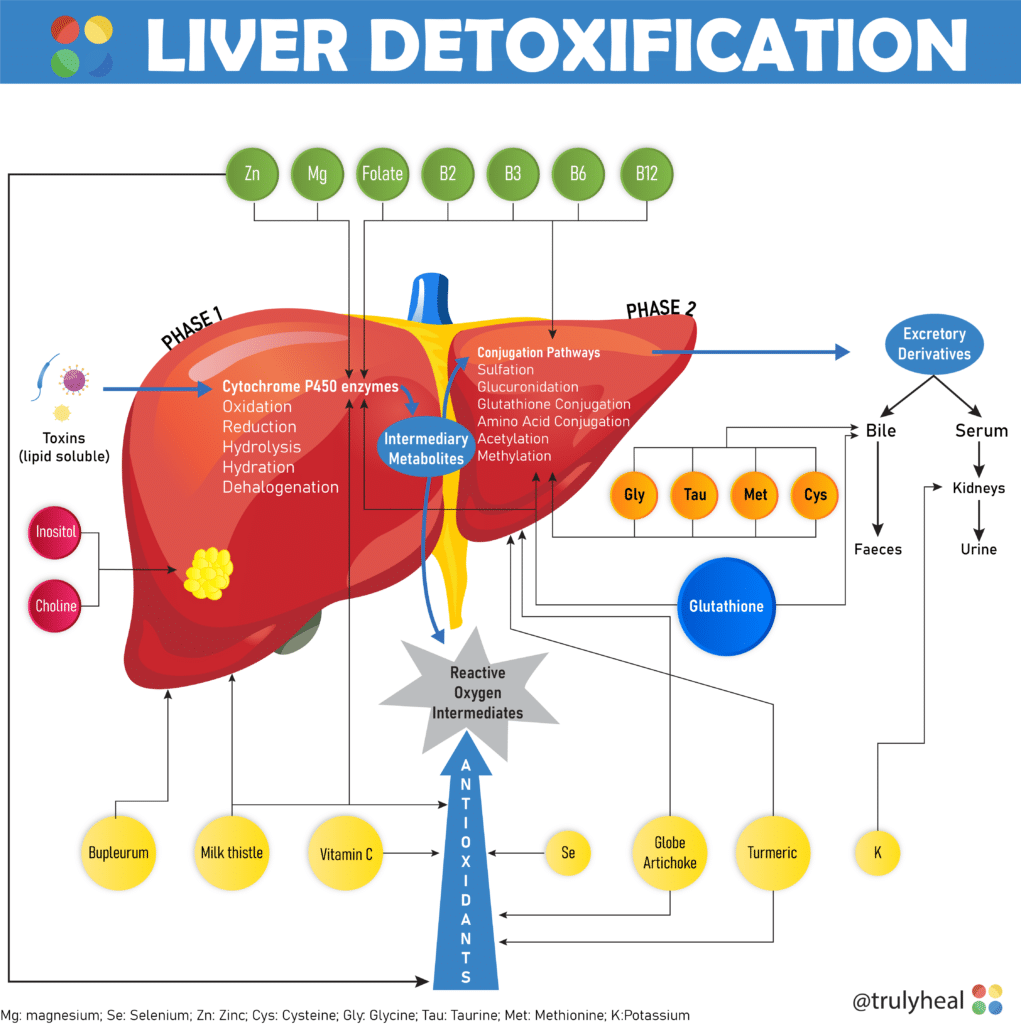
Understanding Colon Cancer
Let’s dive into the world of colon cancer—a significant health concern that affects countless lives. Colon cancer ranks as the third most common cancer-related cause of death in the United States. Colon cancer takes root in the large intestine affects 1 in 23 men and 1 in 25 women at some point in their life. In this article, we’ll learn about colon cancer, explore its signs and symptoms, delve into its root causes, understand treatment options, and arm you with natural strategies to support your well-being.